what happens to the body during ketoacidosis Respiratory/metabolic acidosis vs. alkalosis https://www.facebook.com
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes, which occurs when the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. This happens when the body doesn’t have enough insulin, leading to the breakdown of fat in the body for energy. DKA is a life-threatening condition and requires immediate medical attention. In this post, we will discuss the pathophysiology of DKA and its management. DKA typically occurs in people with type 1 diabetes, but it can also occur in people with type 2 diabetes who have insulin deficiency, such as in cases of severe illness or infections. The hallmark of DKA is hyperglycemia, with blood glucose levels higher than 250 mg/dL, along with the presence of ketones in the blood and urine. The pathophysiology of DKA involves several factors. Firstly, the lack of insulin causes the body to break down fat to use as fuel, leading to the production of ketone bodies as a byproduct. Secondly, the high levels of glucose in the blood draw water from the body’s cells, causing dehydration. Thirdly, the body tries to compensate for the high levels of acid in the blood by breathing rapidly, leading to the characteristic fruity breath odor of DKA. The symptoms of DKA can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, weakness, and confusion. Without prompt treatment, DKA can progress to coma and even death. The management of DKA requires hospitalization and a multidisciplinary approach, including endocrinologists, diabetes nurse educators, and intensive care specialists. The first step in management is to restore fluids and electrolytes to correct dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. This is usually done with intravenous fluids containing saline and potassium, under careful monitoring of fluids and electrolytes, including sodium, chloride, bicarbonate, and phosphorus. Insulin therapy is a key aspect of DKA management, as it helps to lower blood glucose levels and halt the production of ketone bodies. Insulin is usually given as a continuous IV infusion, starting with a bolus of regular insulin, followed by a lower continuous dose to maintain glucose levels within a safe range. Other aspects of DKA management include monitoring for and treating complications such as cerebral edema, cardiac arrhythmias, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and renal failure. In conclusion, DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that requires prompt medical attention. Its pathophysiology involves insulin deficiency, hyperglycemia, ketone body production, dehydration, and acidosis. The management of DKA requires a multidisciplinary approach including fluid and electrolyte replacement, insulin therapy, and careful monitoring for complications. Early recognition and treatment of DKA can prevent serious long-term complications and improve outcomes for people with diabetes.
If you are searching about Diabetic Ketoacidosis | EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Images about Diabetic Ketoacidosis | EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio like Diabetic Ketoacidosis - SimplifiedMed!, Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis / Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka and also Respiratory/Metabolic Acidosis vs. Alkalosis https://www.facebook.com. Read more:
Diabetic Ketoacidosis | EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio
 www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
Respiratory/Metabolic Acidosis Vs. Alkalosis Https://www.facebook.com
 www.pinterest.comacidosis alkalosis nursing metabolic pneumonics gases cardiac imbalances enfermería surg surgical dka pharmacology pathophysiology ketoacidosis diabetes theory cheat nih médico
www.pinterest.comacidosis alkalosis nursing metabolic pneumonics gases cardiac imbalances enfermería surg surgical dka pharmacology pathophysiology ketoacidosis diabetes theory cheat nih médico
Diabetic Ketoacidosis - SimplifiedMed!
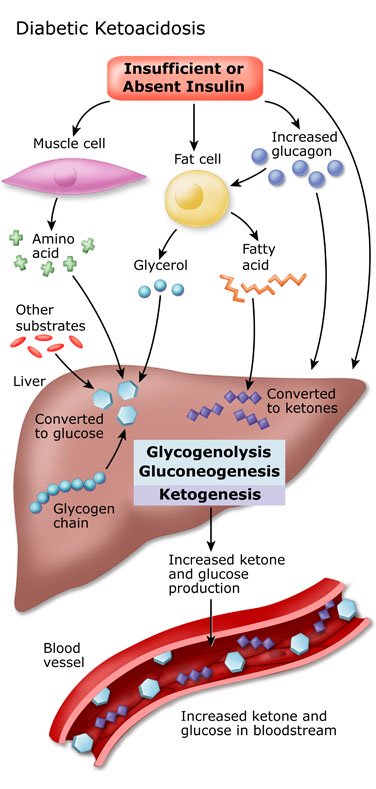 simplifiedmed.weebly.comketoacidosis dka diabética cetoacidosis acidosis mellitus insulin alzheimer pathophysiology diabetica complication stepwards aceitedecoco luchar dtc ucsf metabolism hypoglycemia ketose metabolic
simplifiedmed.weebly.comketoacidosis dka diabética cetoacidosis acidosis mellitus insulin alzheimer pathophysiology diabetica complication stepwards aceitedecoco luchar dtc ucsf metabolism hypoglycemia ketose metabolic
10 Signs And Symptoms That You Are In Ketosis – Infographic
 www.positivehealthwellness.comketosis keto symptoms diet signs effects ketogenic side re if charts tell recipes plan carb positivehealthwellness infographic know easier make
www.positivehealthwellness.comketosis keto symptoms diet signs effects ketogenic side re if charts tell recipes plan carb positivehealthwellness infographic know easier make
Pathophysiology Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis / Diabetic Ketoacidosis Dka
 sraytguh.blogspot.comdiabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology dka starvation jbs elsevierhealth els acidosis correction
sraytguh.blogspot.comdiabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology dka starvation jbs elsevierhealth els acidosis correction
Diabetic ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than. Respiratory/metabolic acidosis vs. alkalosis https://www.facebook.com